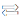A good circuit board, in addition to achieving the principle function of the circuit, but also consider EMI, EMC, ESD (electrostatic discharge), signal integrity and other electrical characteristics, but also to consider the mechanical structure, the heat dissipation of large power consumption chips, on this basis and then consider the aesthetic issues of the board, just like the art of carving, deliberate on every detail of it.
Common PCB layout constraints principles
In the layout of PCB components often have the following considerations.
(1) Does the PCB board shape match the whole machine?
(2) Is the spacing between components reasonable? Are there any horizontal or height conflicts?
(3) whether the PCB needs to be put together? Is the process edge reserved? Are the mounting holes reserved? How to arrange the positioning holes?
(4) How to place the power module and heat dissipation?
(5) Is it convenient to replace the components that need to be replaced frequently? Adjustable components are convenient to adjust?
(6) Is the distance between thermal components and heat generating components considered?
(7) How about the EMC performance of the whole board? How to layout can effectively enhance the anti-interference ability?
For the spacing between components and components, based on the different distance requirements of different packages and the characteristics of Altium Designer itself, if the rules are set to constrain, the settings are too complicated and difficult to achieve. Generally, we draw lines on the mechanical layer to mark the peripheral dimensions of the components, as shown in Figure 9-1, so that when other components are close together, we know roughly their spacing. This is very practical for beginners and enables them to develop good PCB design habits.
.jpg)
By analyzing the above considerations, the common PCB layout constraint principles can be classified as follows.
Component arrangement principle
(1) Under normal conditions, all components should be arranged on the same surface of the PCB, only in the top layer components are too dense, to some limited height and heat generation of small components (such as chip resistors, chip capacitors, chip IC, etc.) on the bottom layer.
(2) in the premise of ensuring electrical performance, components should be placed on the grid and parallel or vertical arrangement with each other, in order to neat and beautiful. Generally do not allow overlapping components, components should be arranged compactly, input components and output components as far away as possible, do not appear to cross.
(3) some components or wires may exist between the higher voltage, they should increase their distance to avoid accidental short circuit caused by discharge, breakdown, layout as much as possible to pay attention to the layout of these signals space.
(4) with high voltage components should be laid out as far as possible in places that are not easily accessible by hand during debugging.
(5) components located at the edge of the board, should try to achieve a distance of two board thickness from the edge of the board.
(6) components on the entire board should be evenly distributed, not this area dense, another area loose, to improve the reliability of the product.
Layout principles in accordance with the signal direction
(1) After placing fixed components, arrange the position of each functional circuit unit one by one according to the signal flow direction, and center on the core component of each functional circuit and carry out local layout around it.
(2) The layout of the components should facilitate the flow of signals, so that the signal as far as possible to maintain a consistent direction. In most cases, the signal flow is arranged from left to right or top to bottom, and the components directly connected to the inputs and outputs should be placed close to the input and output connectors or connectors.
Prevention of electromagnetic interference
.jpg)
(1) for the stronger radiation electromagnetic field components and more sensitive to electromagnetic induction components, they should increase the distance between each other, or consider adding shielding shield to shield.
(2) Try to avoid high and low voltage components mixed with each other and strong and weak signal components interleaved together.
(3) For components that generate magnetic fields, such as transformers, speakers, inductors, etc., the layout should pay attention to reduce the magnetic lines of force on the printed wire cutting, adjacent components should be perpendicular to each other in the direction of the magnetic field to reduce the coupling between them.
(4) Shielding of interference sources or modules susceptible to interference, the shield should be well grounded.
Suppression of thermal interference
(1) for the heat-generating components, should be prioritized in the location conducive to heat dissipation, if necessary, a separate heat sink or small fan can be set up to reduce the temperature and reduce the impact on neighboring components.
(2) Some large power consumption of integrated blocks, high-power tubes, resistors, etc., should be arranged in places where it is easy to dissipate heat, and separated from other components at a certain distance.
(3) thermal components should be close to the measured components and away from the high-temperature area, so as not to be affected by other heat-generating equivalent components, causing misoperation.
(4) double-sided placement of components, the bottom layer is generally not placed on the heating element.
Adjustable components layout principles
For potentiometers, variable capacitors, adjustable inductor coils, micro-switches and other adjustable components layout, should take into account the structural requirements of the machine: if the machine is adjusted outside, its location should be adapted to the location of the adjustment knob on the chassis panel; if the machine is adjusted, it should be placed in the PCB to facilitate the adjustment of the place.




-20x20-20x20.png)