ARM is short for Advanced RISC Machine, which is a 32-bit lean instruction set architecture, but is also equipped with a 16-bit instruction set, generally saving up to 35% over the equivalent 32-bit code, while retaining all the advantages of a 32-bit system.
The main features of ARM processors are.
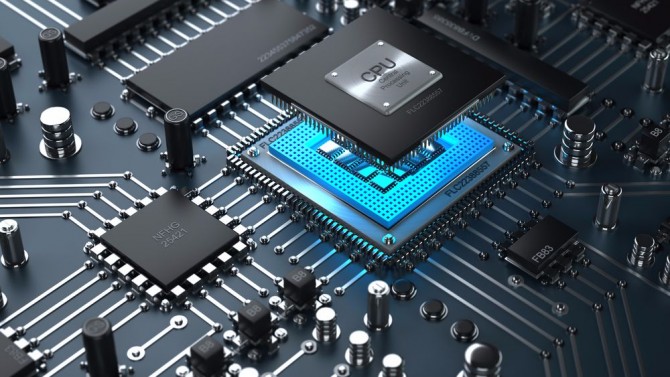
(1) Small size, low power consumption, low cost, high performance - the most important reason why ARM is widely used in embedded systems Support for Thumb (16-bit)/ARM (32-bit) dual instruction set, which is well compatible with 8-bit/16-bit devices.
(2) Extensive use of registers for faster instruction execution.
(3) Most data operations are done in registers.
(4) Flexible and simple addressing methods and high execution efficiency.
(5) Instruction length is fixed.
(6) Load_store structure: In RISC, all calculations are required to be done in the registers. And the communication between registers and memory is done by separate instructions. And in CSIC, the CPU is able to operate on memory directly. Streamline processing method.
MIPS MIPS architecture (English: MIPS architecture, an abbreviation for Microprocessor without interlocked piped stages architecture, also related to Millions of Instructions Per Second), is a processor architecture that takes a streamlined instruction set (RISC), emerged in 1981, developed and licensed by MIPS Technologies, and is widely used in many electronic products, networking devices, and other applications. It is widely used in many electronic products, networking devices, personal entertainment devices, and business devices. The earliest MIPS architecture was 32-bit, and the latest version has become 64-bit.
The basic features of MIPS are.
(1) contains a large number of registers, instruction numbers, and characters.
(2) Visual pipeline delay time slots.
These features allow the MIPS architecture to deliver the highest performance per square millimeter and the lowest power consumption of any SoC design today.
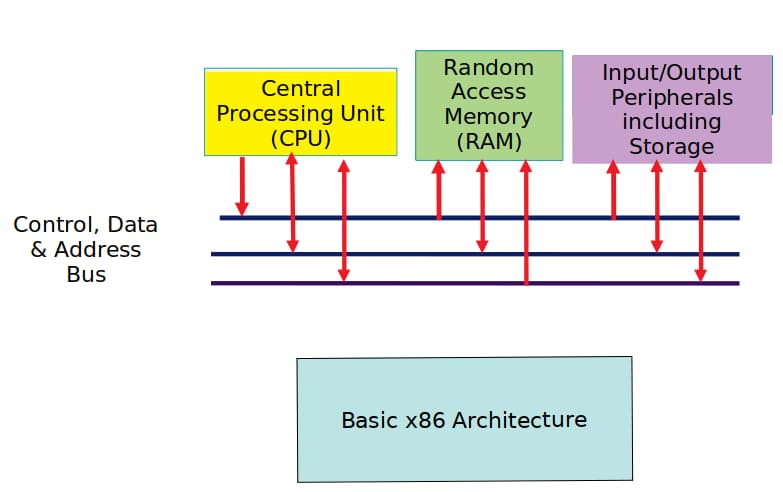
X86 The X86 architecture is a generic term for a microprocessor architecture designed and manufactured by the chip giant Intel. If you don't understand this, then I'm sure you will when I say words like 8086, 80286, etc. It is based on this that the name X86 architecture is widely known. Today, most of the PCs we use are X86 architecture. This shows the popularity of X86 architecture, which is also closely related to Intel's dominant position. The x86 uses the CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer) architecture. Unlike RISC, in a CISC processor, the instructions of a program are executed sequentially and serially, and the individual operations in each instruction are executed sequentially and serially. The advantage of sequential execution is simple to control, but the utilization of each part of the computer is not high and the execution speed is slow.




-20x20-20x20.png)